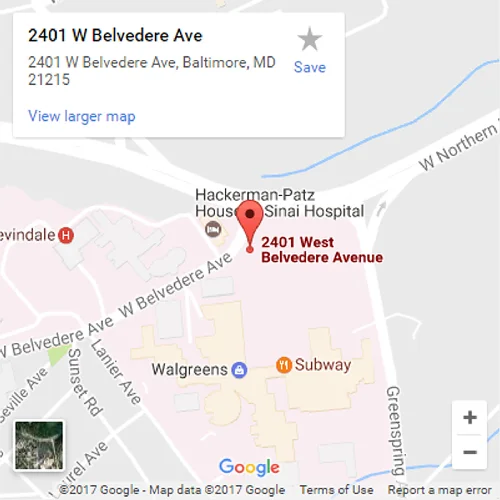
Multiple Drill-hole Osteotomy
Multiple Drill-hole Osteotomy of the Femur
This illustration shows an example of a multiple drill-hole osteotomy technique for a corticotomy in the distal femur (near the knee). A corticotomy is a bone-cutting technique that preserves the nearby bone vessels and periosteum (the tissue that covers the surface of bones). Several drill passes are made before an osteotome (a chisel-like bone-cutting tool) is used to complete the corticotomy.
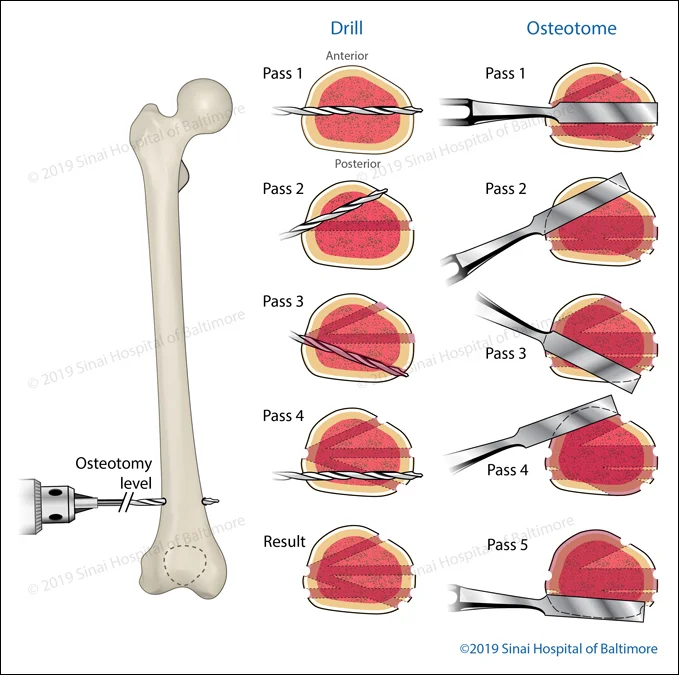
Focal Dome Osteotomy of the Supramalleolar Ankle
The focal dome osteotomy allows the surgeon to improve the patient’s bony alignment with a precise multiple drill-hole technique performed in an arc-like pattern. After the drill holes are made, an osteotome (a chisel-like bone-cutting tool) is used to complete the alignment. Internal or external fixation is added to maintain the correction. The following illustrations and fluoroscopic (intra-operative) images describe this procedure in the lower leg (tibia and fibula) near the ankle.
- A. Deformity analysis: Analyze the angles of the lower tibia. (LDTA, Lateral distal tibial angle.)
- B. Deformity analysis: Define the axes, apex, and magnitude of the deformity.
- C1., C2. Focal dome osteotomy: Multiple drill holes are performed with a focal dome guide.
- D. The fibular osteotomy is performed through a small incision below the level of the multiple drill holes in the tibia. The guide pins for screw placement are accurately positioned before osteotomy completion.
- E. The osteotome allows for a low-energy fibular osteotomy, which improves the healing potential after correction. Multiple osteotomes are used to connect the tibial drill holes before a through and through osteotomy is completed.
- F. Displacement of the tibia and fibula with an osteotome ensures the osteotomy is complete.
- G1., G2. Acute alignment of proximal and distal axes is performed.
- H1., H2. Internal fixation is utilized to maintain correction.