Home » Conditions » Congenital Femoral Deficiency (CFD) » SUPERhip Reconstruction with 130° Blade Plate for Congenital Femoral Deficiency Patients
SUPERhip Reconstruction with 130° Blade Plate for Congenital Femoral Deficiency Patients
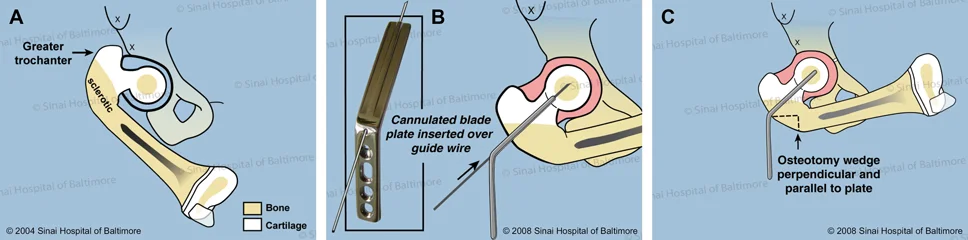
- A. This is a patient with congenital femoral deficiency with delayed bone formation in the neck of the femur.
- B. A blade plate is inserted into the center of the femoral head over a wire.
- C. In the first osteotomy (bone cut), a triangular piece of bone is removed from the side of the femur.
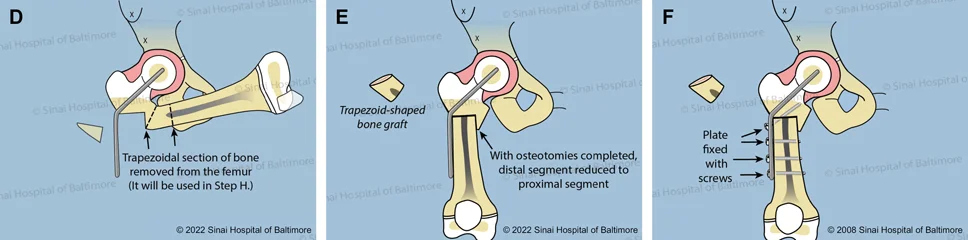
- D. The second bone cut removes a trapezoid-shaped piece of bone.
- E. The two ends of the femur are joined, and the orientation of the femur and knee is normalized.
- F. The femur shaft is secured to the plate with screws.
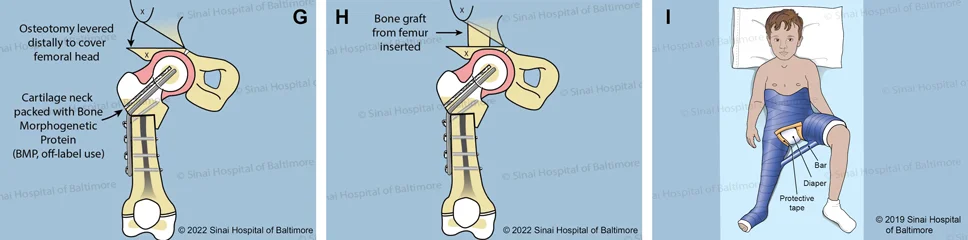
- G. A channel in the bone is created parallel to the blade plate, and it is filled with bone morphogenetic protein (BMP). This off-label use of BMP stimulates the growth of new bone. A Dega osteotomy is performed to provide coverage to the femoral head.
- H. The trapezoid-shaped bone graft, taken from the earlier bone cut (D.), is used to stabilize the Dega osteotomy.
- I. A spica cast is used to protect the bone for six weeks while the bone heals.